Table of Contents
T1: Introduction to the MatCalc graphical user interface (GUI)
This tutorial was tested on
MatCalc version 6.04 rel 1.001
license: free
database: none
This first tutorial provides a brief tour of MatCalc's graphical user interface. The interface elements that will be referred to in the subsequent tutorials, are introduced here. At the end, the very basic operations with a workspace and a working directory are demonstrated.
Contents
- Appearance of the graphical user interface
- Menus and toolbar
- Console window
- Configuring the layout of the GUI
- The 'File' menu
- Creating a new workspace file
- Modifying the working directory
- Adding workspace information
- Saving and closing files
- Getting help
The graphical user interface
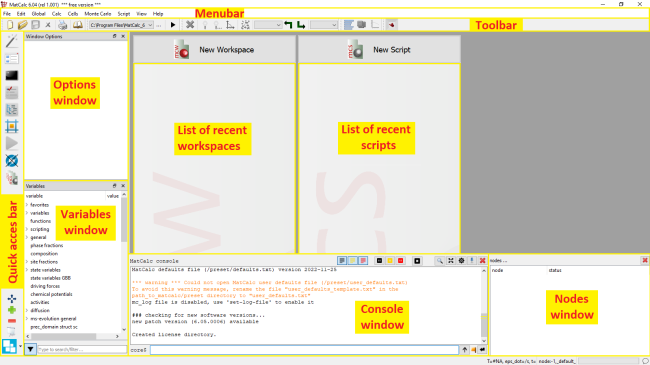
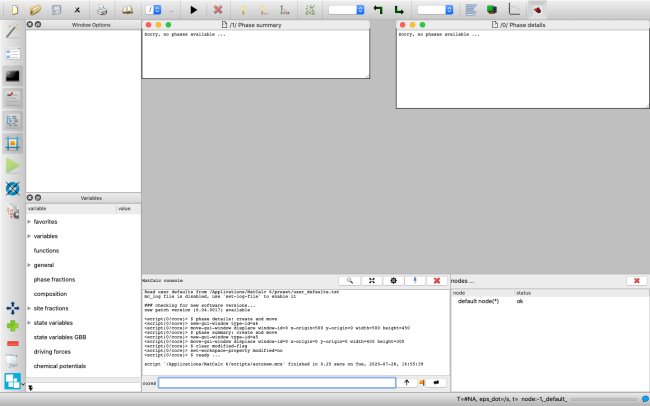
Screen layout
When MatCalc is first opened, the screen appears as shown below (Windows version).
The table below gives brief descriptions of the different areas of the screen.
| Menu bar | The main menu (see below and the relevant section in the Reference book). |
|---|---|
| Toolbar | Icons giving quick access to frequently used functions (see below) |
| Quick access bar | Icons giving quick access to window management options (see below). |
| Console | This window has an area that shows output from calculations and other operations, as well, as an area for entering command-lines; more information is given below and in Tutorial 12. |
| Options window | Context-sensitive options to change the way information is displayed. Tutorial 2, Tutorial 4 and Tutorial 5 give more information about the Options window. |
| Variables window | A list of MatCalc's built-in variables with their current values. See Tutorial 4 and Tutorial 5 for more about variables. |
| Nodes window | List of nodes used in simulation. Multiple nodes are used in advanced calculations. |
| Status bar | Gives information on the current state of the system (temperature, time, etc.) and on the contents of graphical windows (see Tutorial 4). |
| List of recent workspaces | List of recently opened MatCalc workspaces. Clicking on the item on the list will open the relevant workspace. |
| List of recent scripts | List of recently opened MatCalc scripts. Clicking on the item on the list will allow to edit the relevant script (see Tutorial 13). |
Menu bar
As with any typical GUI application, this gives access to a number of sub-menus. The File and Help menus are documented in this tutorial, and the contents of the other menus will be described in more detail in subsequent tutorials.
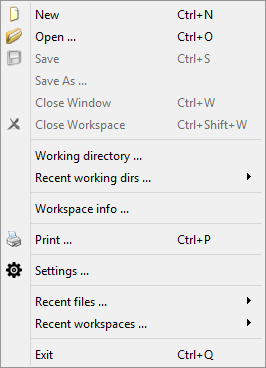
| File | opening, saving and closing files (see 'File operations' below) |
|---|---|
| Edit | text-editing commands such as undo, redo, cut, copy, paste |
| Global | commands for setting up the system (see Tutorial 2 and subsequent tutorials) |
| Calc | commands for the most frequent types of calculation (see Tutorial 2 and subsequent tutorials) |
| Cells, Monte Carlo | commands for starting calculation within additional MatCalc modules |
| Script | to run scripts (more on this in Tutorial 13) |
| View | to configure the GUI and create new windows for the display of results (see Tutorial 4 and Tutorial 5) |
| Help | see Getting help below |
On platforms running under MacOS an additional menu mcg is also present. Comprehensive information about the menu items can be found in the reference book.
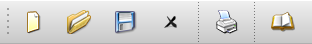
Toolbars
The toolbar area contains a number of icon groups:
File
Working directory and script
Edit
Calculation

L-R: Stop current action, single equilibrium, stepped equilibrium, search phase boundary, precipitate kinetics calculation, select calculation state, save into current calculation state, load from current calculation state, select calculation buffer.
Manage windows
Managing toolbar elements
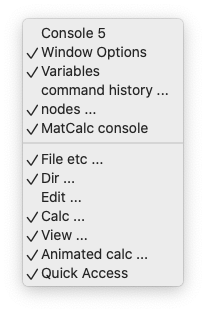
Right-clicking on the toolbar area gives a menu allowing the user to control which windows and which icon groups are to be displayed on the screen:
Quick access bar
The quick access bar enables you to customise the appearance of your MatCalc session by displaying, hiding and rearranging the windows.
The table below gives brief descriptions of the different areas of the screen.
Configuring the layout
In addition to the display options described above, icon groups and the 'Options', 'Variables', 'Nodes' and 'Console' windows can be detached from their locations and rearranged as desired by dragging and dropping. In this case, they are given title bars similar to that of the 'MatCalc console'. The 'Console', 'Options', 'Variables' and 'Command History' windows can also be attached to or detached from the left-hand column area as required.
Menu bar right-click menu
Right-clicking on the menu bar brings up a menu allowing the user to show or hide menu icon groups and windows as described above ('Managing toolbar elements').
View > Show
Enables the following windows to be displayed or hidden: 'console' (F4), 'options' (F3), 'variables' (F2), 'node manager' (Shift + F5)
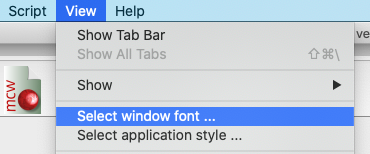
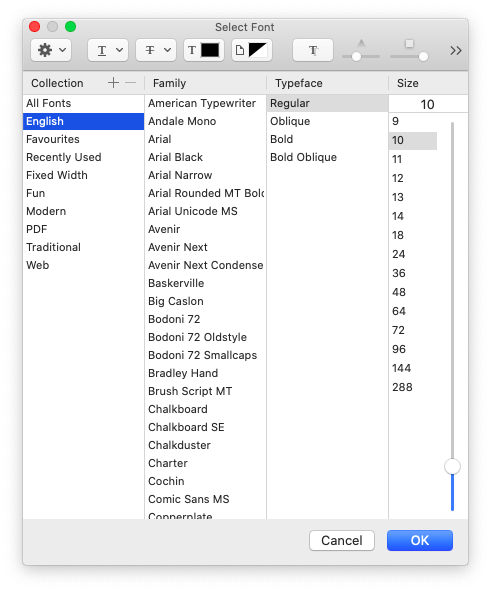
View > Select window font
Here the user can select an alternative font/font size for the display of numerical output. This does not affect the appearance of the 'console', 'nodes', 'options' and 'variables' windows.
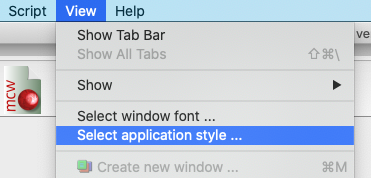
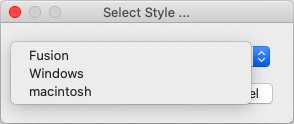
View > Select application style
The overall appearance of MatCalc can be modified here. The different options offer a greater or lesser degree of free space around text items, stronger or more subtle contrast etc. - experiment until you find an option that suits you.
View > Display window IDs
This switches the numbers /0/, /1/, /2/, etc. in the top left-hand corner of the output windows.
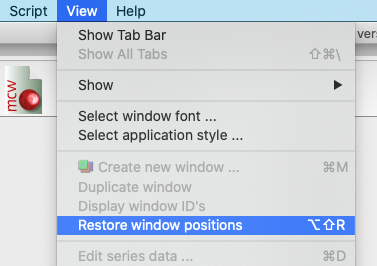
View > Restore window positions (Alt + Shift + R)
View > Windows
Using this menu, the output windows can be brought to the front (if hidden behind others) or restored to their original size (if minimised).
File operations
Having inspected most GUI elements, let’s have some interaction with MatCalc. In this section, a MatCalc workspace will be handled. A working directory will be specified also.
The 'File' menu
Creating a new workspace file
The workspace is the basic element for any activity in MatCalc GUI. It contains all the necessary information on the user calculations, comprising inputs (elements, phases, compositions, thermodynamic and mobility data) and outputs (results of calculations, graphs, etc.). Saving the workspace preserves all this information for future use.
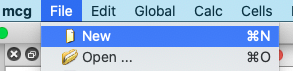
To create a new workspace, do one of the following:
- Click on 'New' from the 'File' menu
- Press Ctrl + N on the keyboard
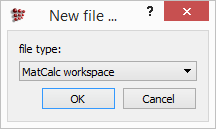
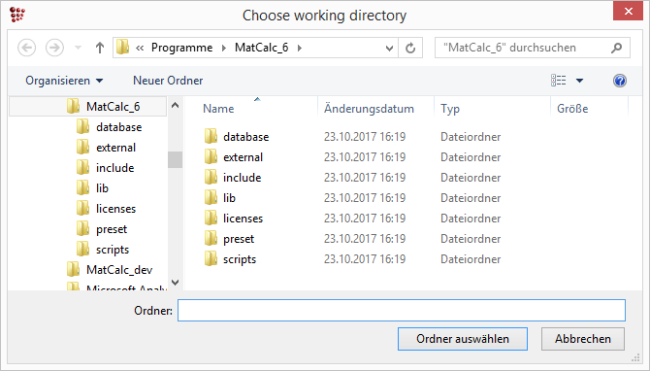
The following dialogue box will appear (except when clicked on 'New Workspace' button):
Select 'MatCalc workspace' from the drop-down list. This runs a script file called autonew.mcs, which makes two additional windows appear: Phase details and Phase summary. When the new workspace is first created, the Phase summary and Phase details windows show messages indicating that no phases have yet been selected. The workspace is now ready for thermodynamic or precipitation calculations to be set up and performed.
Working directory
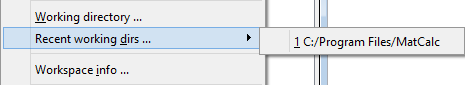
The working directory is the directory opened by default when MatCalc is saving any output files or looking for any input files. Clicking on 'Working directory…' in the 'File' menu allows the user to designate an existing directory as the working directory or to create a new directory for this purpose. MatCalc remembers your chosen working directory for next time.
The paths of the current working directory and of recently used working directories are listed to the right of Recent working dirs…, allowing any of these directories to be selected easily.
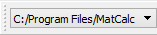
The same information is also available in a drop-box in the toolbar area:
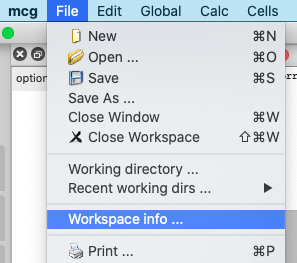
Adding workspace information
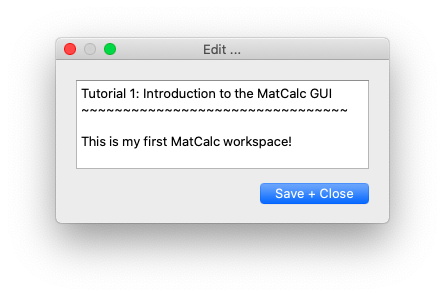
Clicking on Workspace info… in menu File opens a box in which information about the current workspace can be entered. This is useful for details of the assumptions used in the calculation, the sources of experimental data, etc.
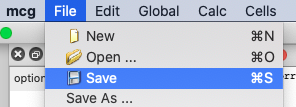
Saving workspace
Workspaces can be saved using alternatively:
- Save… in the menu File
- the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + S
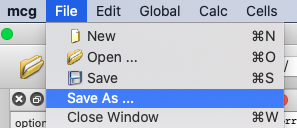
To save an existing workspace under a different name, select Save As… from the file menu.
Close workspace
To close a workspace, do one of the following:
- choose Close Workspace from the file menu
- press Ctrl + Shift + W
WARNING
Getting help
The MatCalc help files are accessible on this website. At present, no local installation is provided.
In the Console, typing a question-mark will display a list of available commands. These will be discussed in more detail in Tutorial 12.
Subsequent articles
The tutorial is continued in Tutorial 2 - Calculating a single equilibrium
Go to the MatCalc tutorial index.